
Knowing IRS tax filing deadlines is crucial for individuals and businesses to avoid unnecessary penalties and interest. Missing these deadlines can result in significant financial consequences, including late filing and payment penalties, as well as accrued interest on unpaid taxes. For instance, if you owe taxes and fail to file or pay by the deadline, you may face a late filing penalty of up to 5% of the unpaid taxes per month and a late payment penalty of 0.5% per month. Additionally, interest on unpaid taxes compounds daily, further increasing the amount owed.
Understanding the key tax filing dates helps taxpayers plan and manage their financial obligations effectively. The primary deadline for filing individual federal income tax returns is typically April 15, unless it falls on a weekend or holiday. Businesses, such as partnerships and corporations, have different deadlines, often earlier in the year. For those needing more time, filing an extension (Form 4868) can provide a six-month reprieve until October 15. Staying informed about these deadlines ensures compliance with IRS regulations and minimizes potential financial penalties.
Why knowing IRS tax filing deadlines is crucial
This knowledge helps taxpayers avoid penalties and plan their financial obligations more effectively. It also ensures that they can take advantage of deductions and credits available to them, which can significantly reduce their tax liability.
Consequences of missing deadlines (penalties, interest, etc.)
Missing deadlines can lead to substantial penalties and interest. For example, late filing penalties can be up to 5% of the unpaid taxes per month, while late payment penalties are typically 0.5% per month. Interest on unpaid taxes compounds daily, adding to the total amount owed.
Overview of the important dates for tax filing in the US
Key dates include the primary deadline for individual federal income tax returns, usually April 15, and earlier deadlines for businesses. Additionally, taxpayers can file for an extension to extend their filing deadline to October 15.
What Are IRS Tax Filing Deadlines?
Definition of Tax Filing Deadlines:
Tax filing deadlines are specific dates by which taxpayers must submit their tax returns to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). These deadlines are crucial for ensuring compliance with tax laws and avoiding penalties.
Why They Are Set by the IRS:
The IRS sets these deadlines to maintain order and efficiency in the tax collection process. By having a uniform deadline, the IRS can manage the influx of tax returns and ensure that taxpayers have a clear timeline for filing and paying their taxes.
Key Factors That Affect Deadlines:
Several factors can influence tax filing deadlines:
- Filing Status: Individual taxpayers typically file by April 15, while businesses like partnerships and S corporations have earlier deadlines, often March 15.
- Extensions: Taxpayers can file Form 4868 to extend their deadline by six months, typically until October 15.
- Fiscal Year vs. Calendar Year: Businesses operating on a fiscal year have different deadlines based on their fiscal year-end.
- Natural Disasters: In areas affected by federally declared disasters, the IRS may extend deadlines for filing and paying taxes.
- Holidays: If the deadline falls on a weekend or holiday, it is moved to the next business day.
Key Tax Filing Deadlines

a. Deadline for Individual Tax Returns (Form 1040)
The standard deadline for filing individual federal income tax returns (Form 1040) is April 15 of each year. If April 15 falls on a weekend or holiday, the deadline is moved to the next business day. This deadline applies to most individuals, including employees, retirees, and those with simple tax situations.
b. Extended Filing Deadline (Form 4868)
To extend the filing deadline, individuals can file Form 4868, which provides an automatic six-month extension until October 15. This extension allows more time to file the tax return but does not extend the payment deadline. If taxes are owed, an estimated payment should be made by the original April deadline to avoid penalties and interest.
c. Estimated Quarterly Tax Payments for Self-Employed Individuals
Self-employed individuals, including independent contractors and gig workers, must make estimated quarterly tax payments on the following due dates:
- April 15 for the first quarter (January 1 – March 31)
- June 15 for the second quarter (April 1 – May 31)
- September 15 for the third quarter (June 1 – August 31)
- January 15 of the following year for the fourth quarter (September 1 – December 31).
These payments are necessary to avoid penalties for underpayment of taxes throughout the year.
d. Filing for Nonprofit Organizations
Tax-exempt organizations must file Form 990 annually. The deadline is the 15th day of the fifth month after the end of their fiscal year. For organizations on a calendar year, this typically means a deadline of May 15. Nonprofits can file for an extension using Form 8868, which extends the deadline to November 15 for calendar-year filers.
e. Deadlines for Business Taxes (Corporations, Partnerships, LLCs)
- Corporate Tax Filing Deadlines (Form 1120): For C corporations with a calendar year-end, the deadline is April 15. Corporations can file Form 7004 for an extension, which typically extends the deadline to October 15.
- Partnerships and LLCs (Form 1065): The deadline for partnerships and multi-member LLCs is the 15th day of the third month after the end of their tax year. For calendar-year entities, this is March 17. An extension can be filed using Form 7004, extending the deadline to September 15.
Special IRS Filing Deadlines for Taxpayers Abroad

Standard Deadline vs. Extended Deadline for Overseas Taxpayers
U.S. citizens and resident aliens living abroad are granted an automatic two-month extension to file their federal income tax returns. This means their deadline is typically June 15, but if this date falls on a weekend or holiday, it is moved to the next business day, such as June 17 in 2024. However, any taxes owed are still due by April 15, and interest accrues on unpaid balances after this date.
How to File from Abroad
Filing taxes from abroad requires careful consideration of mailing and time zones. Taxpayers can file electronically, which is faster and more reliable than mailing paper returns. For those who must mail their returns, it’s essential to ensure timely delivery by using a trackable shipping method and allowing sufficient time for international mail.
Taxpayer Tips for Avoiding Late Filing When Living Overseas
To avoid late filing penalties:
- Plan Ahead: Ensure you understand the extended deadline and any additional extensions available.
- File Electronically: This method is faster and reduces the risk of lost or delayed returns.
- Attach Required Statements: If using the automatic extension, include a statement explaining your eligibility.
- Pay Taxes on Time: Even with an extension to file, taxes are due by April 15 to avoid interest and penalties.
What Happens If You Miss the Filing Deadline?
Penalties for Late Filing and Late Payment
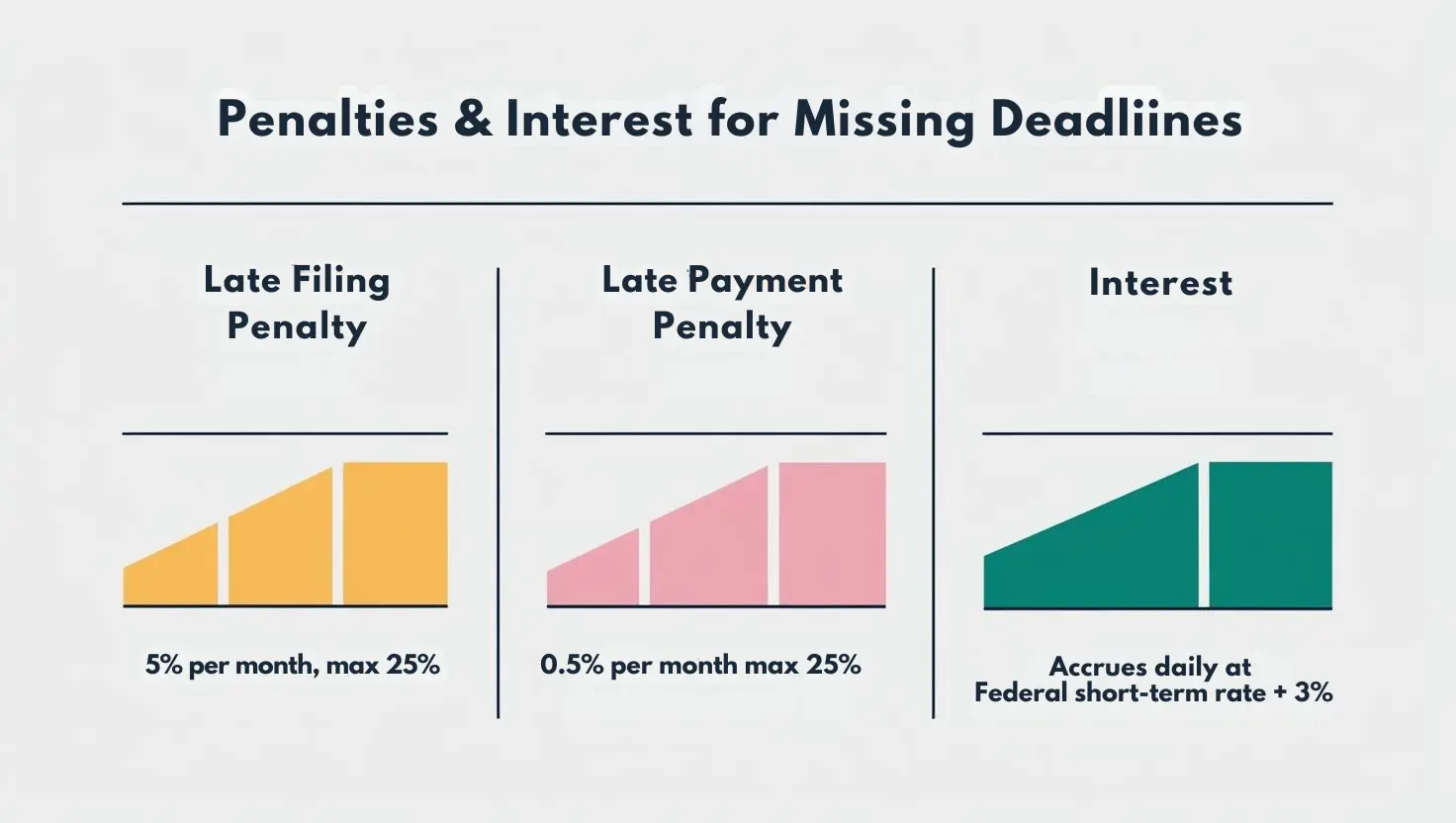
Missing the IRS filing deadline can result in significant penalties. The late filing penalty is typically 5% of the unpaid taxes for each month or part of a month that the return is late, up to a maximum of 25%. If you also fail to pay your taxes on time, a late payment penalty of 0.5% per month applies, up to 25%. When both penalties apply, the combined rate is 5% per month (4.5% for late filing and 0.5% for late payment). If your return is more than 60 days late, the minimum penalty is $510 (for tax returns required to be filed in 2025) or 100% of the tax due, whichever is less.
How the IRS Calculates Interest and Penalties
The IRS calculates penalties based on the unpaid tax amount and the time elapsed since the deadline. Interest accrues daily on unpaid taxes, starting from the original due date, and is compounded daily. The interest rate is typically the federal short-term rate plus 3%. Both penalties and interest continue to accumulate until the tax is fully paid.
Steps to Take If You Miss the Deadline
If you miss the deadline:
- File as Soon as Possible: Submit your return to minimize additional penalties and interest.
- Pay Any Taxes Owed: Make a payment to reduce the amount of late payment penalties and interest.
- Consider an Installment Agreement: If unable to pay the full amount, set up a payment plan with the IRS

How Filing Early Can Save You Money
Filing your taxes early can save you money by avoiding late filing and payment penalties. It also ensures that you receive any refund due to you sooner. Additionally, early filing helps prevent interest from accruing on unpaid taxes, reducing the total amount you owe over time.
Important Tax Deadlines for Tax Credits and Refunds
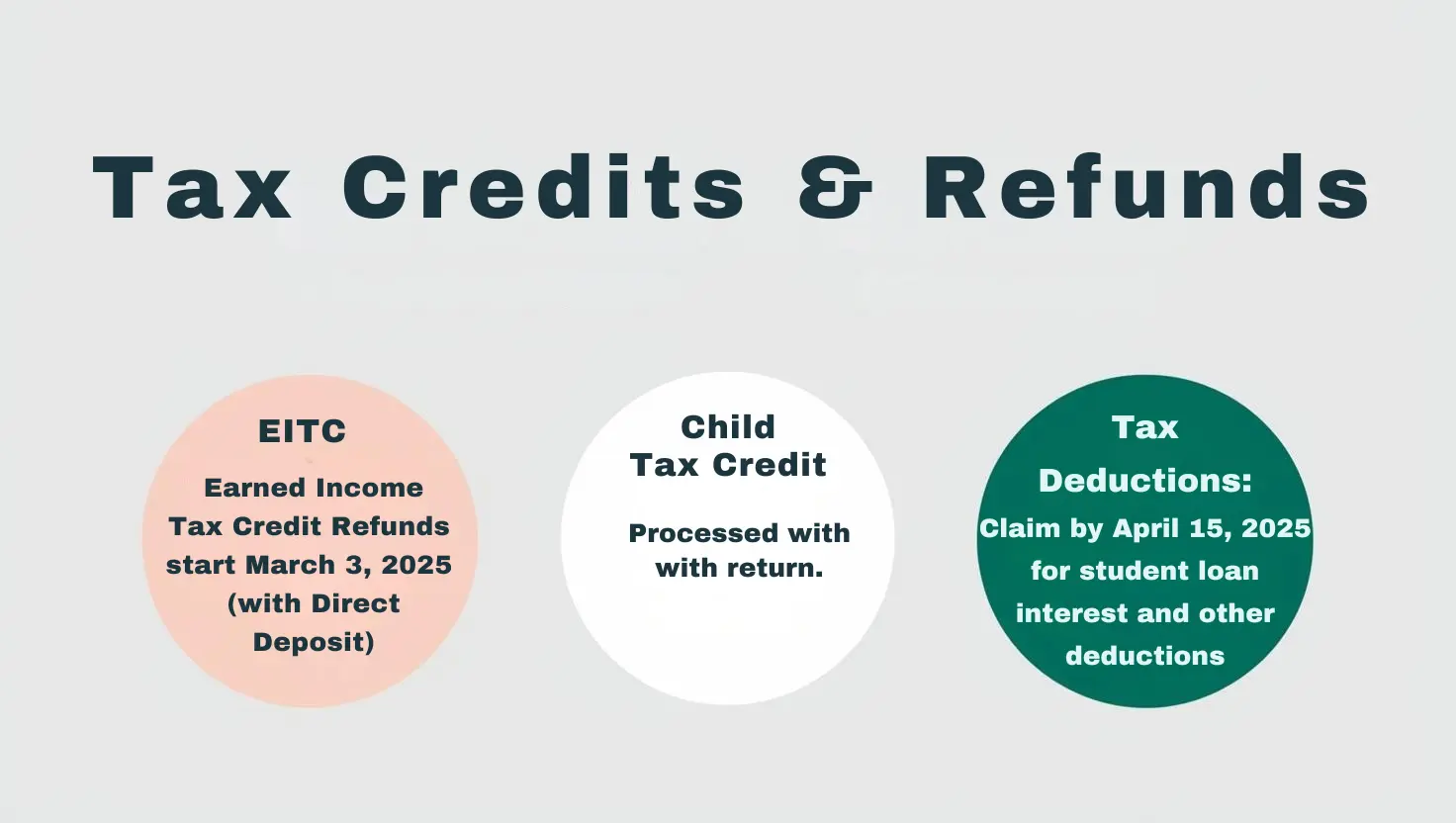
Key Dates for Claiming Tax Credits
- Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) and Additional Child Tax Credit (ACTC): Refunds for these credits will be issued starting March 3, 2025, if filed early with direct deposit. The IRS typically cannot issue refunds before mid-February for returns claiming these credits, but processing begins earlier for those who file electronically and choose direct deposit.
- Child Tax Credit: Similar to the ACTC, refunds for the Child Tax Credit are processed with the return and may be delayed if claiming the ACTC.
Filing Deadlines for Refunds and How to Request Them
To receive a refund, taxpayers must file their tax return by the standard deadline of April 15, 2025, or request an extension to October 15, 2025. Refunds are typically issued within 21 days of e-filing, but paper returns take longer1. To expedite refunds, taxpayers should file electronically and choose direct deposit.
Deadlines Related to Tax Deductions
- Student Loan Interest and Tuition Deductions: These deductions can be claimed on the tax return filed by April 15, 2025. There are no specific deadlines for these deductions beyond the standard filing deadline.
- Other Deductions: Most deductions, such as mortgage interest and charitable contributions, must be claimed by the standard filing deadline. If an extension is needed, it applies to filing the return but not to claim deductions, which must be documented and claimed within the extended filing period.
How to Stay on Top of IRS Deadlines

Setting Reminders for Key Dates
To stay on top of IRS deadlines, it’s essential to set reminders for key dates. This can be done using digital calendars or specialized software like File In Time or Jetpack Workflow, which help track and manage deadlines efficiently. Setting reminders ensures that you never miss important filing dates, such as the April 15 deadline for individual tax returns or quarterly estimated tax payments.
Using IRS Tools to Track Deadlines
The IRS provides several tools to help taxpayers track deadlines:
- IRS Calendar: Available on the IRS website, this calendar lists important tax-related dates.
- Mobile Apps: The IRS2Go app allows taxpayers to check their refund status and access tax information on the go.
- Where’s My Refund? Tool: This tool helps track the status of tax refunds.
Benefits of Working with a Tax Professional
Working with a tax professional can significantly help ensure that deadlines are met:
- Expert Knowledge: Tax professionals are well-versed in IRS regulations and deadlines, reducing the risk of missed filings.
- Streamlined Process: They often use advanced software to manage client deadlines efficiently, ensuring timely filings and minimizing penalties.
- Personalized Support: Tax professionals can provide customized advice and reminders tailored to your specific tax situation, helping you stay compliant with IRS requirements.
Conclusion
Recap of Key IRS Tax Filing Deadlines
Key IRS tax filing deadlines include April 15 for individual federal income tax returns (Form 1040), with an extension available until October 15 by filing Form 4868. Businesses, such as partnerships and S corporations, typically file by March 17, while C corporations file by April 15. Self-employed individuals must make estimated quarterly tax payments on April 15, June 15, September 15, and January 15 of the following year.
Importance of Being Proactive to Avoid Penalties
Being proactive is crucial to avoid penalties and interest. Missing deadlines can result in significant financial consequences, including late filing and payment penalties, as well as accrued interest on unpaid taxes. Staying informed about deadlines and planning ahead helps ensure compliance with IRS regulations.
Final Tips on Staying on Track with Filing Deadlines
To stay on track:
- Use IRS Tools: Utilize the IRS calendar and mobile apps to track deadlines.
- Consult a Tax Professional: Consider hiring a professional to manage complex tax situations and ensure timely filings.
- File Electronically: Electronic filing is faster and reduces errors, helping you avoid delays and penalties.
